03/02/2026 10:05 p.m.
https://stage.cablematic.com/en/products/2xpci2xpci-express-expansion-box-expresscard-CR094/
https://stage.cablematic.com/en/products/2xpci2xpci-express-expansion-box-expresscard-CR094/
2xPCI/2xPCI-Express Expansion Box (ExpressCard)
REF: CR094
Specifications
- Speedidad transfer ExpressCard 250Mb/s.
- Compatible with ExpressCarrd Rev-1.0a.
- ExpressCard Advanced Error Reporting to support ECRC.
- It has 2 x 32-bit PCI slots 33MHz via PCIe. PCI slots have a transmission rate of 133 MB/s.
- It has 2 x PCIe 1X. The PCIe slots have a transmission rate of 250 MB/s.
PVP
€165.31
Price including VAT:
€165.31
PVD
€137.22
PVP: Retail price.
Check conditions.
PVP: Sale price to distributors.
Check conditions.
warranty
returns
safe
Specifications
- Speedidad transfer ExpressCard 250Mb/s.
- Compatible with ExpressCarrd Rev-1.0a.
- ExpressCard Advanced Error Reporting to support ECRC.
- It has 2 x 32-bit PCI slots 33MHz via PCIe. PCI slots have a transmission rate of 133 MB/s.
- It has 2 x PCIe 1X. The PCIe slots have a transmission rate of 250 MB/s.
Keywords
Did not find what you were looking for? These topic could help you
More info
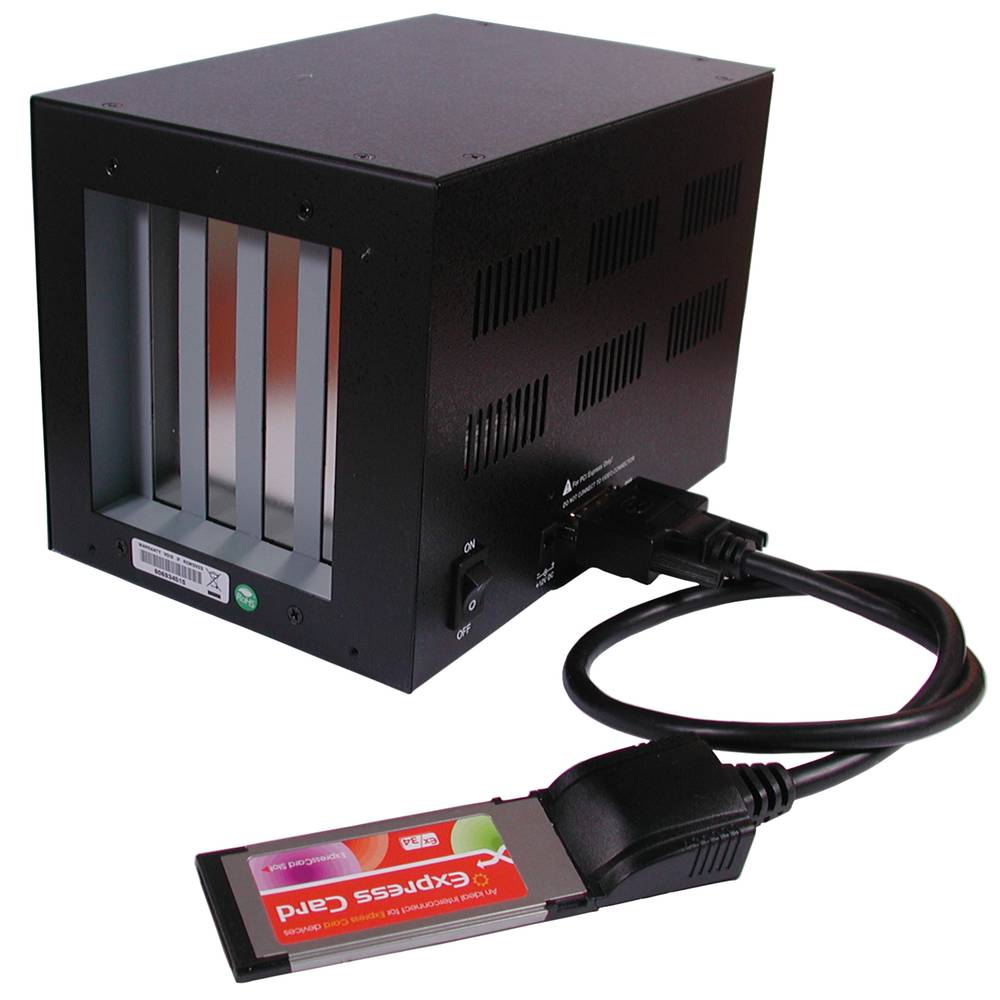
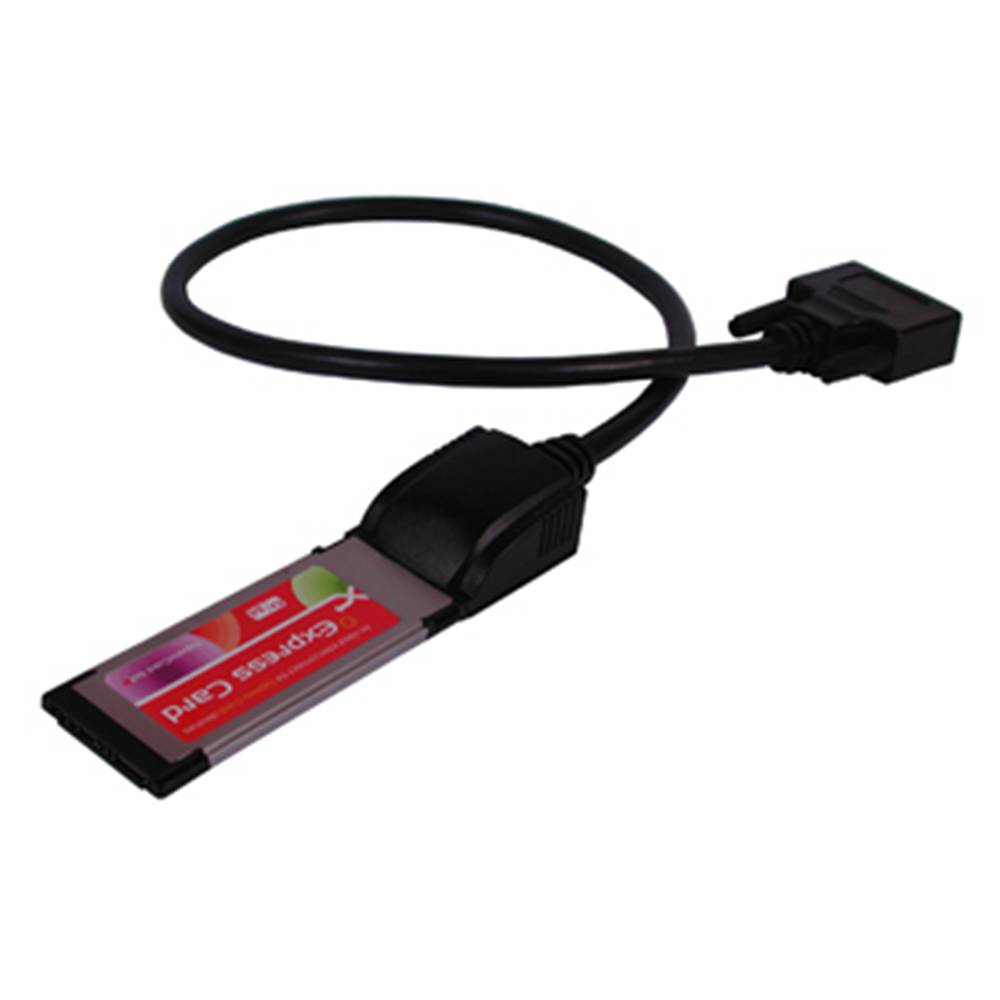
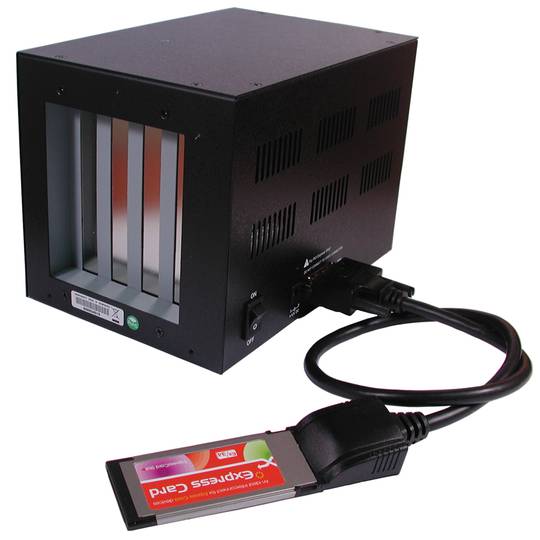
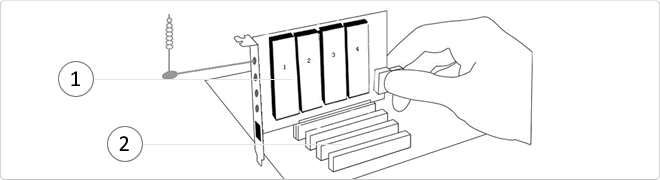
external box that allows to accommodate inside two PCI cards and 2 32-bit PCI-Express 1X cards. This external box connects to an ExpressCard slot using a special card provided. Ideal for laptops that do not have PCI slots or if you want to share several PCI cards with multiple PCs, thus providing an external box PCI and PCIe cards.
Specifications
- Speedidad transfer ExpressCard 250Mb/s.
- Compatible with ExpressCarrd Rev-1.0a.
- ExpressCard Advanced Error Reporting to support ECRC.
- It has 2 x 32-bit PCI slots 33MHz via PCIe. PCI slots have a transmission rate of 133 MB/s.
- It has 2 x PCIe 1X. The PCIe slots have a transmission rate of 250 MB/s.
- PCI supports 3.3V and 5.0V cards.
- LengthMaximum cable 2m.
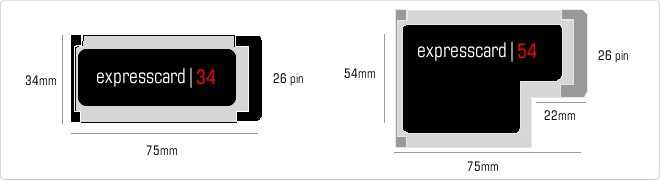
- ExpressCard in 34mm format.
- It requires external power supply (included).
- metal housing for added strength.
- PnP compliant PCI IRQ conflict free or ports E/S.
- Size: 20.6 x 13.7 x 14.3 cm.
- Gross Weight: 2.4 kg
- Number of packages: 1
Technical terms
- PCI - MiniPCI
- Expresscard
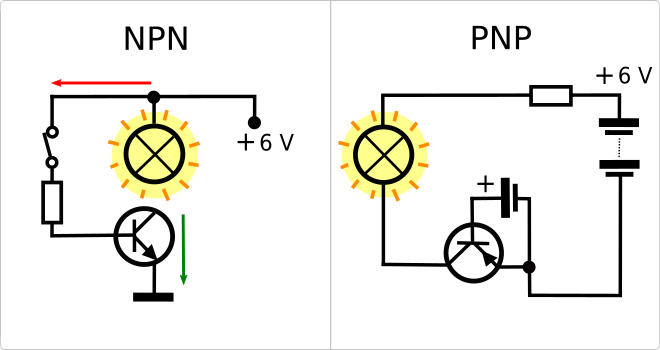
- Differences between PNP and NPN
PCI - MiniPCI
A Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI, "Peripheral Component Interconnect") is a bus (picture 2) computer standard for connecting peripheral devices directly to your motherboard. Dimensions of the cards - PCI (standard) 107 mm x 312 mm (picture 1) - PCI Low Profile Height: 36.07 mm x 64.41 mm Depth: 119.91 mm to 167.64 mm - Mini PCI Mini PCI cards have a Maximum consumption2W.