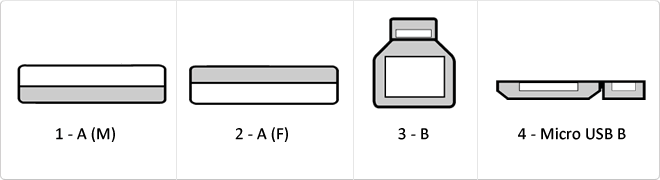
USB
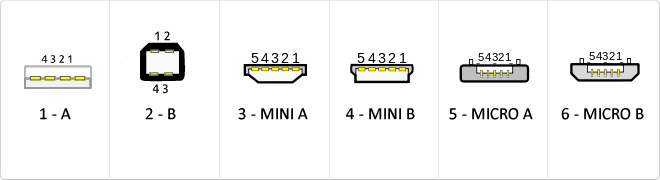
The USB (Universal Serial Bus) is a standard that defines the cables, connectors and used a bus to connect, communicate, computers, peripherals and electronic devices protocols Transmission Rates Low speed (USB 1.0). Transfer rate up to 1.5 Mbit/s (188 kB/s) used in keyboard, mouse ... transfer rate up to 12 Mbit/s (1.5 MB/s) High Speed ??(USB 2.0): Rate transferencia up to 480 Mbit/s (60 MB/s) SuperSpeed ??(USB 3.0) transfer rate up to 4.8 Gbit/s (600 MB/s) Connector Types 1 - USB type A (4 pin) 2. - USB type B (4 pin) 3 - Mini A (5-pin) 4 - Mini B (5-pin) 5 - Micro A (5-pin) 6 - Micro B (5-pin)
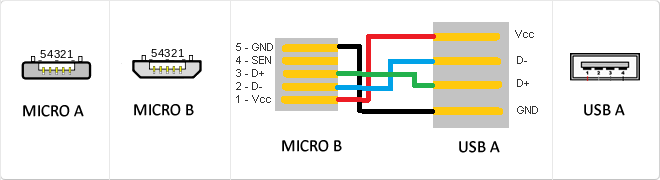
MicroUSB
or horizontal. The micro USB with five pins, which pins identification (ID) Micro AB USB connectors special work. AB connectors with pin ID can allow the device to function as a connector A or B to standard USB technology. This gives the new smart phones and other devices the option to act as either a single storage device or as provi
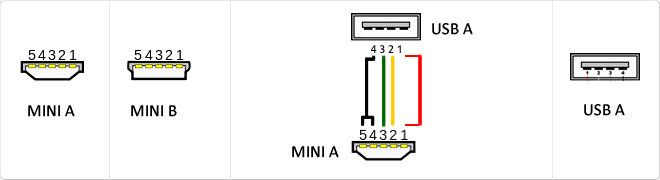
Mini USB
The mini USB connectors are smaller than their standard counterparts and have USB fifth pin. The fifth pin is known as the pin ID and is typically not used in mini USB connectors. It was designed to allow later improved USB technology. The mini USB connectors have a cycle life of at least 5000 connections and disconnections, which accommodates the mobile nature of the devices that are designed to interact. The standard USB connectors are generally used with devices that are stationary and not disconnected often.
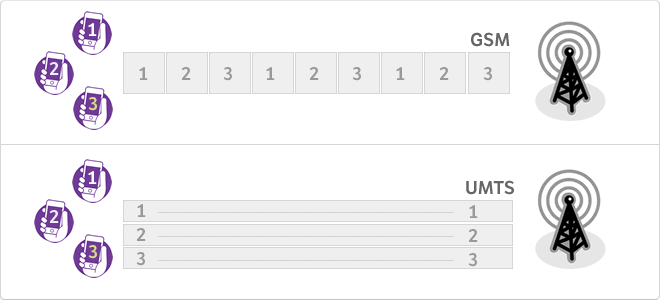
GSM
The global system for mobile communications (English Global System for Mobile communications, GSM, and originally from the French groupe spécial mobile) is a standard system, royalty-free, digital mobile phone. A GSM client can connect through your phone to your computer and send and receive emails, faxes, surf the Internet, access to the computer network security acompany (LAN/Intranet) and use other functions of digital data, including short message service (SMS) or text messages. What are the differences between GSM and UMTS? The GSM system operates by TDMA, ie, time is divided into slots and each user is assigned a slot, ie, a period for which data can be transmitted. Therefore each channel is shared by a ndetermined number of users. The system is a UMTS (WCDMA) code division multiple access broadband. In this system there are no time slots and GPRS. All users transmit simultaneously on the channel, but each user signals are encoded with a unique code so that even though we think that an "indecipherable signal" is formed by using the same frequencies simultaneously, It is not toyes, because the base station is capable of decoding and re perfectly separate each of the communications received from different users. This obviously implies a much higher channel utilization, to not share in time.
![]()
USB 3.0
USB 3.0 is the second major revision of the standard Universal Serial Bus (USB) connectivity for computing. USB 3.0 has transmission speeds of up to 5 Gbit/s, which is 10 times faster than USB 2.0 (480 Mbit/s). Connector Types 1 - USB type A plug 2 - 3 USB type A female - USB type B 4 - Micro USB B
dBi
The dBi isotropic or decibel is a unit for measuring the gain of an antenna in reference to a theoretical isotropic antenna. The value dBi corresponds to the gain of an ideal antenna (theoretical) radiating the received power of a device to which it is connected, and which also transmits the signals received from space without regard either external or additional gains or losses powers.
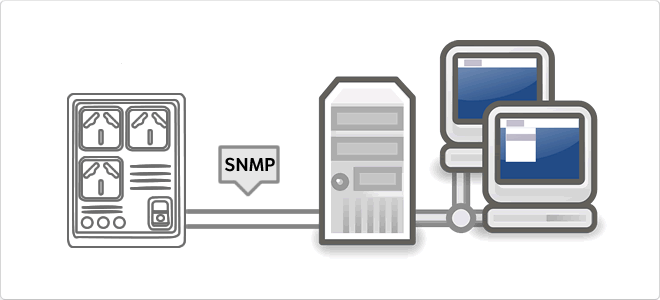
SNMP
The Simple Network Management Protocol, or SNMP (English Simple Network Management Protocol) is a protocol for the application layer that facilitates the exchange of management information between network devices. It allows administrators to monitor network performance, find and solve problems, and plan for growth. In an attempt to explain in a simple way, we could imagine that instala card using SNMP to monitor a UPS on a network.
DHCP
(DHCP stands for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, in Spanish "protocol Dynamic Host Configuration") is a network protocol that allows clients to obtain an IP network configuration parameters automatically. It is a protocol for client/server where a server usually has a list of dynamic IP addresses and will allocate these customers as they are left freeKnowing at all times who has been in possession of that IP, how long it has had and who has been assigned later.
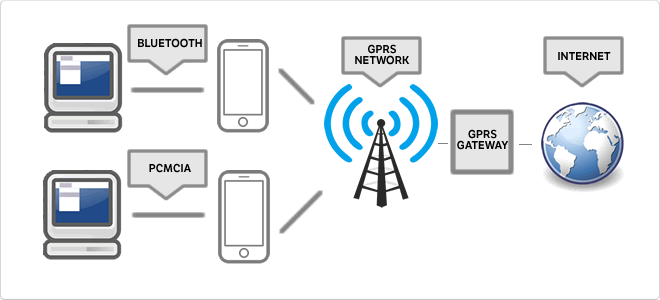
GPRS
General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) or general packet radio service created in the 80s is an extension of the Global System for Mobile Communications (Global System for Mobile Communications or GSM) for the transmission of data by packet switching. A similar service for mobile phones, the IS-136 system. It allows transfer rates of 56-114 kbps. These Class A devicesThey can simultaneously use GPRS and GSM services. Only Class B may be connected to one of the two services at all times. While GSM service (voice or SMS) is used, the GPRS service, which automatically restarts when the GSM service ends is suspended. Most mobile phones are of this type. Class C are alternately connected to one or another service. Switching between GSM and GPRS shouldperformed manually.
UMTS
Universal mobile telecommunications system (Universal Mobile Telecommunications System or UMTS) is one of the technologies used by mobile third-generation successor to GSM, because the GSM technology itself could not follow an evolutionary path to get to providing services considered third generation. Although initially is designed for use in mobile phones, the UMTS network is not LIMITADaa these devices and it can be used by others. What are the differences between GSM and UMTS? The GSM system operates by TDMA, ie, time is divided into slots and each user is assigned a slot, ie, a period for which data can be transmitted. Therefore each channel is shared by a number of users. The system is a UMTS (WCDMA) code division multiple access dand broadband. In this system there are no time slots and GPRS. All users transmit simultaneously on the channel, but each user signals are encoded with a unique code so that even though we think that an "indecipherable signal" is formed by using the same frequencies simultaneously, It is not, because the base station is capable of decoding and re perfectly separate each of the communicationsreceived from different users. This obviously implies a much higher channel utilization, to not share in time.
![]()
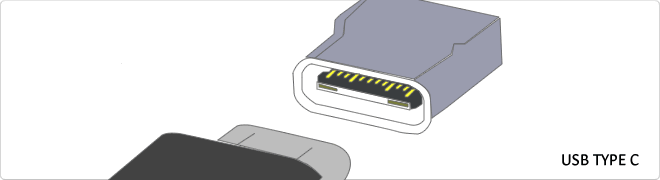
Reversible USB Type-C
USB-C reversible USB version called USB cables USB Type C Type C or USB reversible. The important thing is this type of USB is that it has top and bottom. So you may save the blows that are given involuntarily to connect the connector upside down. It is also characterized in that when connected will make an audible "click". The USB-C or reversible USB cables can reach 10 Gbps and support USB 3.0, 3.1Use is estimated up to 10,000 applications and has some measures 8.4mm x 2.6mm is also compatible with USB 3.1 and USB indicate creators
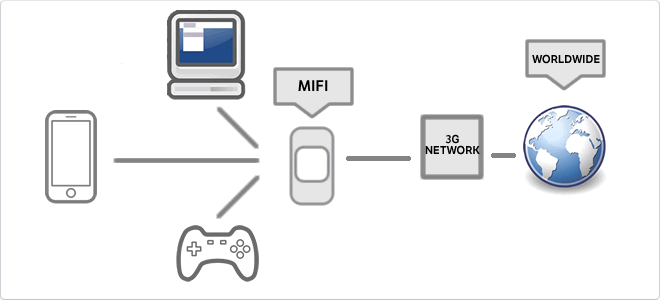
MiFi
MiFi is a mobile router that acts as an access point to the Internet via 3G or later. You can connect to one or more devices at once by WiFi. It can be used with multiple WiFi devices such as desktops, laptops, tablets, smartphones, etc.
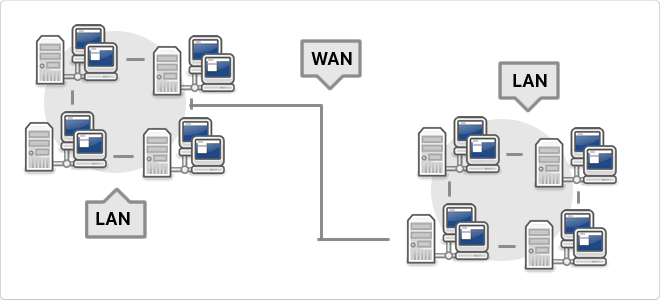
WAN
WAN, which is also known as wide area network is a network that consists of several private computers or organizations. Today with the speed that is in LANs is no longer necessary to use WAN
RJ45
When we talk about RJ45 ("Registered Jack" 45) we refer to a telecommunications network interface for wired connection of voice and data equipment.
This connector has 8 pins or connections and may have a specific category depending on the data transfer speed and bandwidth (category 5e, 6, etc.)
The common application is their use in Ethernet network cables under TIA/EIA-568-B standard that defines the arrangement of pins (pinout), but can also be used for other applications.
- Direct pin diagram:
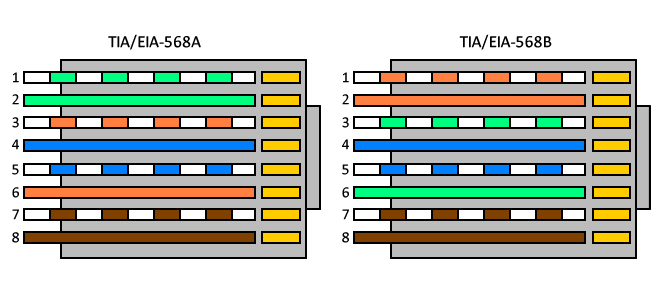
EIA-568A
Pin No.1: WHITE-GREEN
Pin No.2: GREEN
Pin No.3: WHITE-ORANGE
Pin No.4: BLUE
Pin No.5: WHITE-BLUE
Pin No.6: ORANGE
Pin No.7: WHITE-BROWN
Pin No.8: BROWN
EIA-568B
Pin No.1: WHITE-ORANGE
Pin No.2: ORANGE
Pin No.3: WHITE-GREEN
Pin No.4: BLUE
Pin No.5: WHITE-BLUE
Pin No.6: GREEN
Pin No.7: WHITE-BROWN
Pin No.8: BROWN
- Schematic of crossed pins:
The crossover cable has one end with EIA-568A scheme and the other one with EIA-568B.
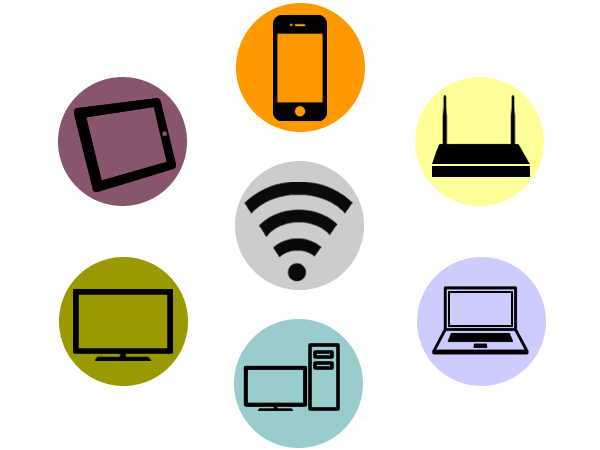
Wifi
The Wifi technology is a wireless communication mechanism between devices. This technology allows you to connect devices such as computers, laptops, mobile etc... to the Internet or communicate with the devices themselves.
Applications can be several, among the most common are the access points, ideal for giving and sharing a connection signal to multiple devices. It is the typical configuration of a home user.
Repeater, ideal to repeat and amplify weak signal.
The power and range between devices basically depends on the antenna and its hardware.
The wireless signals work under a unified standard regulations, the standard that is based on the IEEE 802.11. These include IEEE 802.11b, IEEE 802.11g and IEEE 802.11n working at 11 Mbit/s, 54 Mbit/s and 300 Mbit/s, respectively.
Being any device with a standardized protocol such technology can connect to another using the same technology, making it a kind of universal connection.
The wireless networks are characterized by the ease and convenience of making connections in infrastructure, since it is not necessary to perform network cable installations.
it also allows connecting a lot of devices to a single node.
![]()