10/18/2025 8:41 p.m.
https://stage.cablematic.com/en/products/power-supply-for-modbus-module-din-rail-35-mm-12-vdc-3-a-TJ091/
https://stage.cablematic.com/en/products/power-supply-for-modbus-module-din-rail-35-mm-12-vdc-3-a-TJ091/
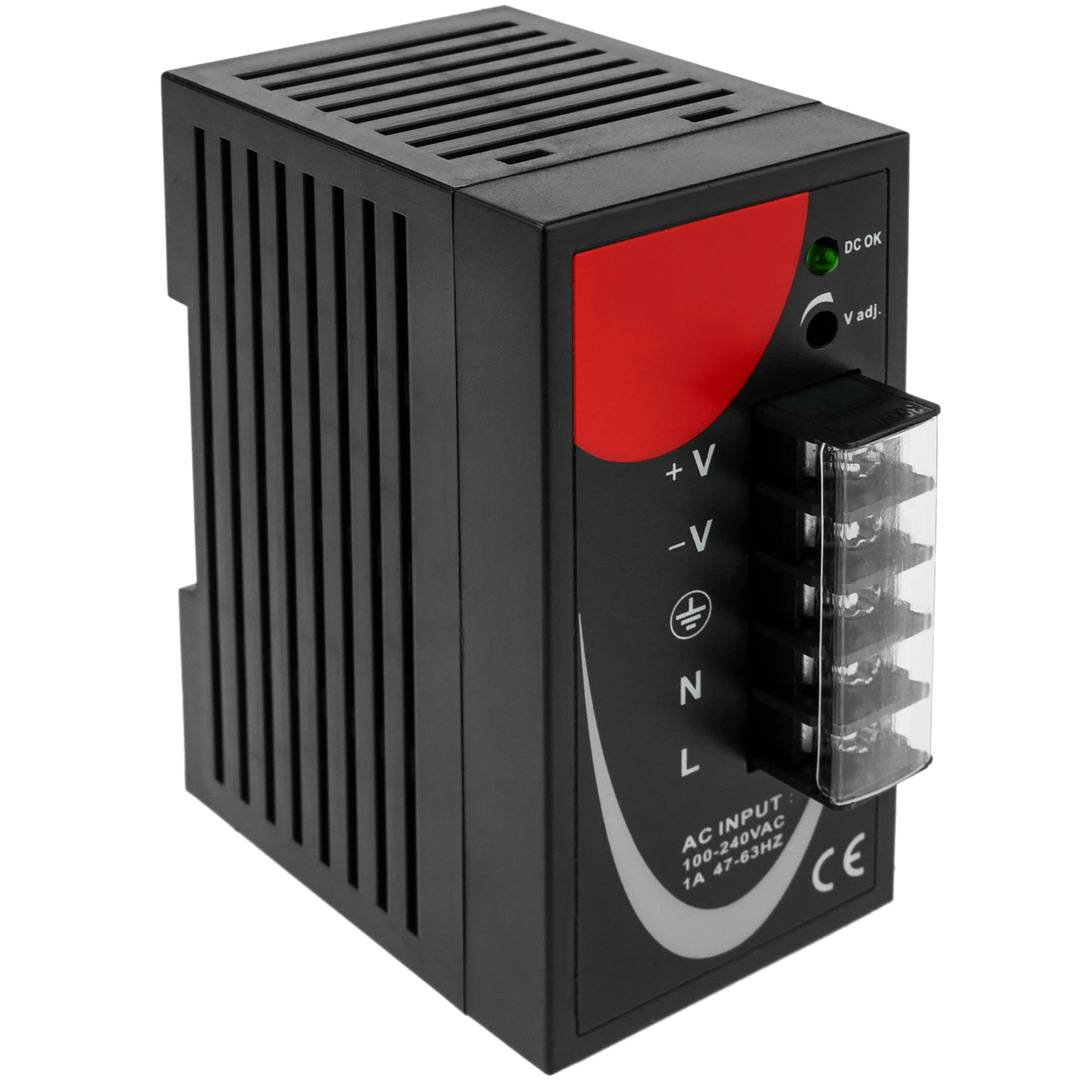
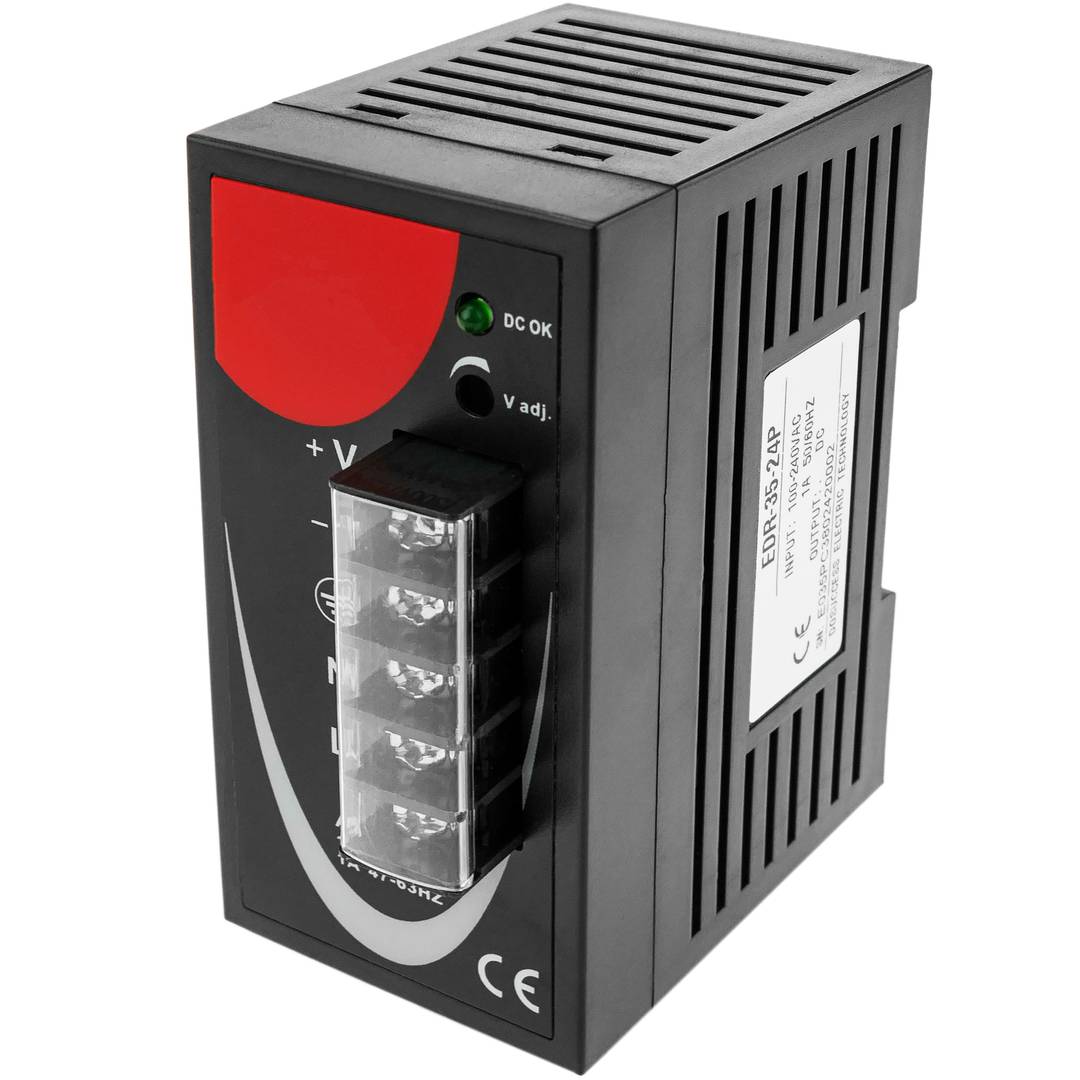
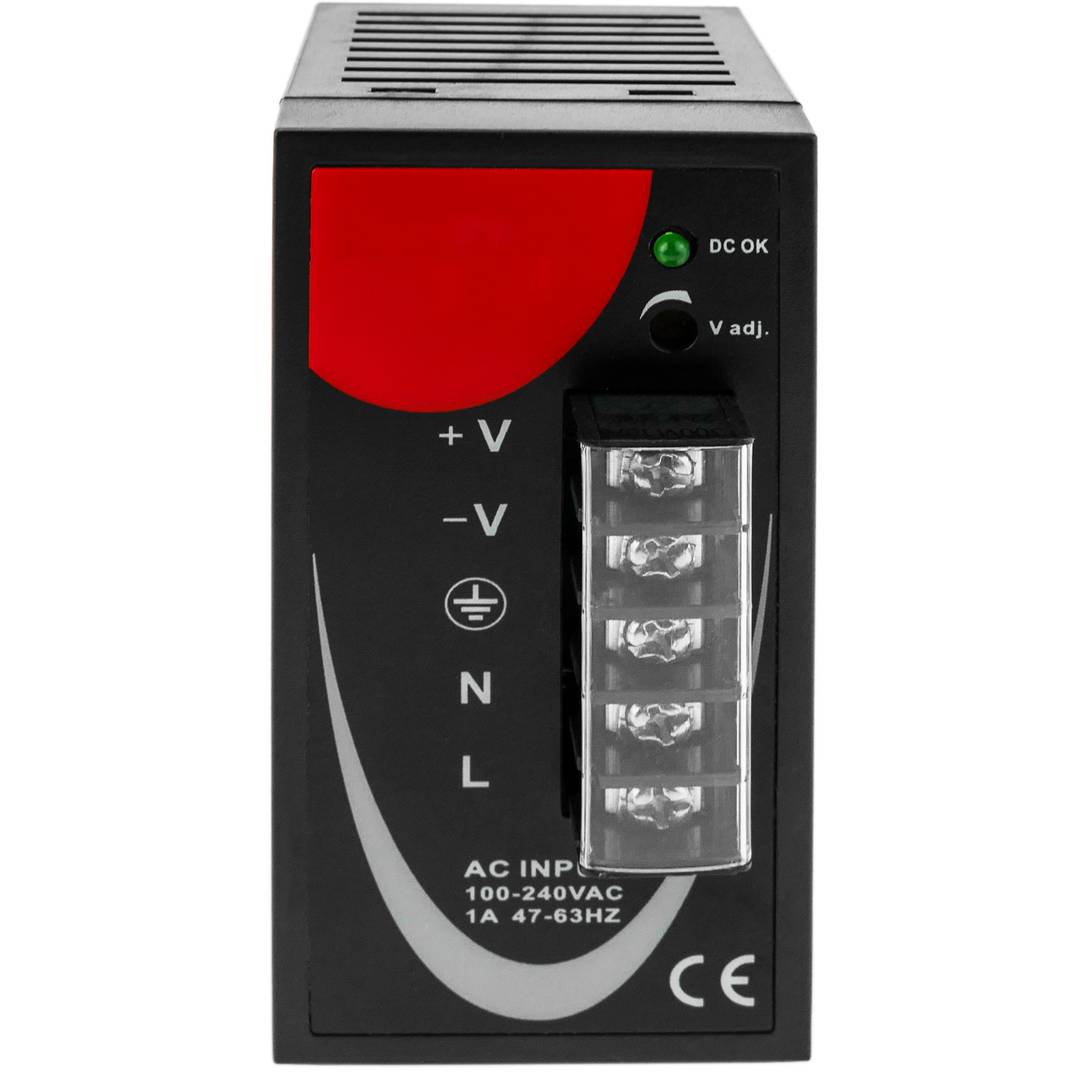
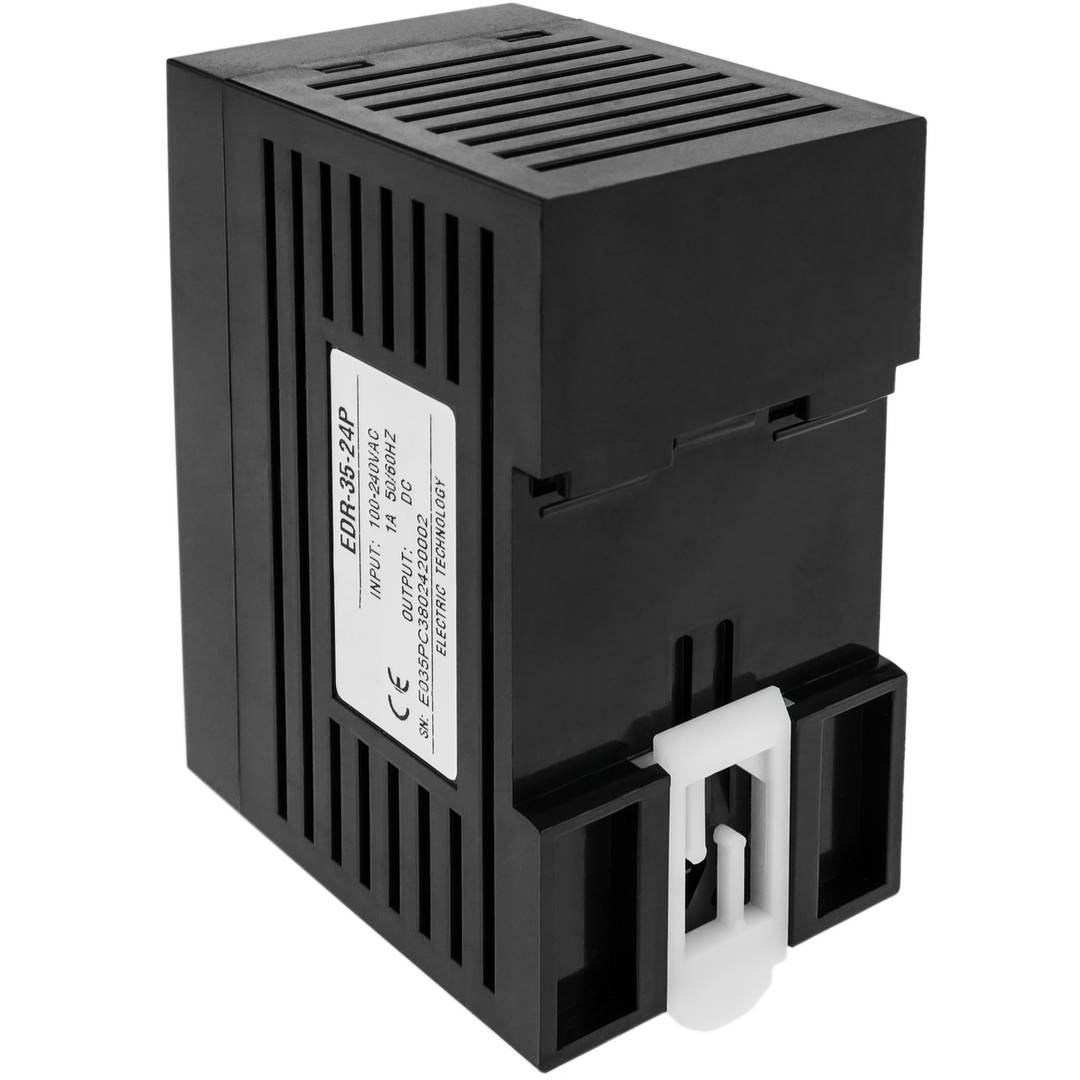
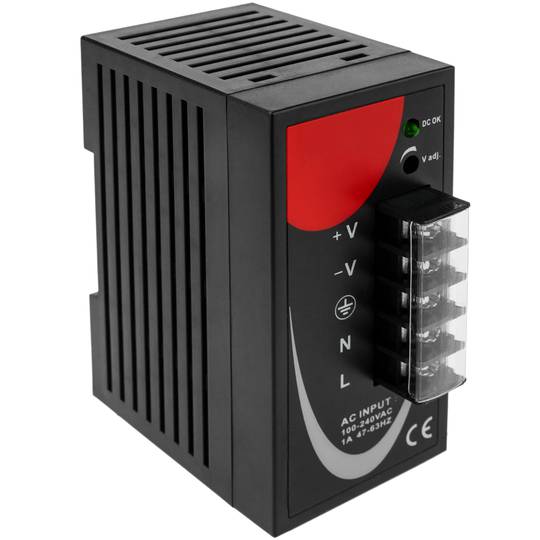
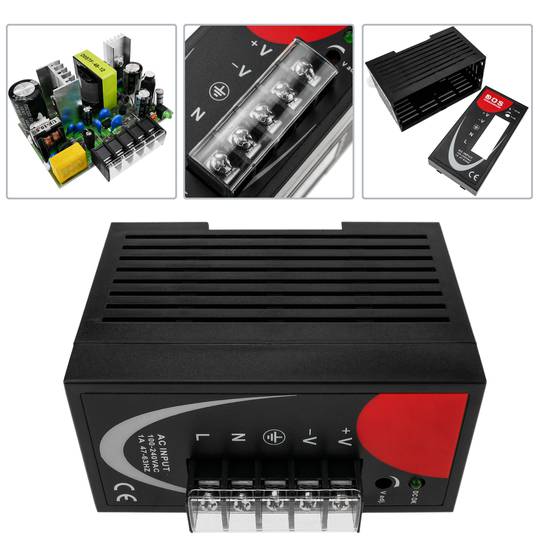
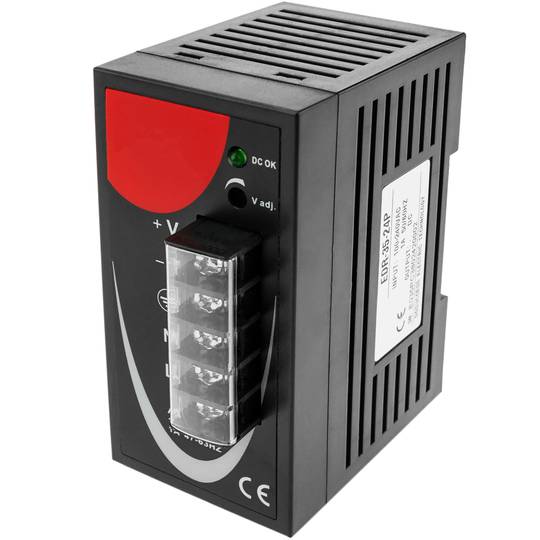
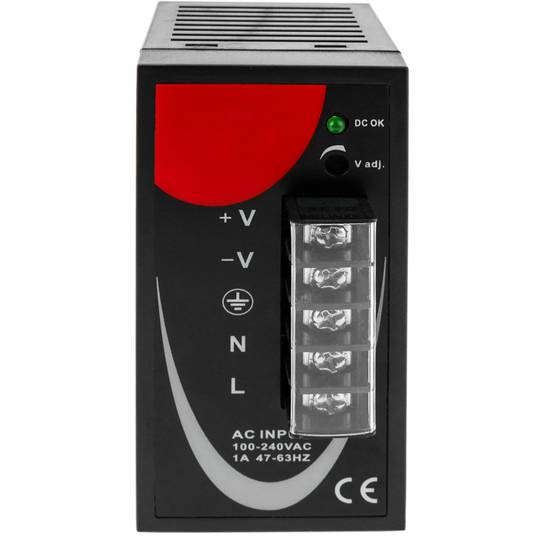
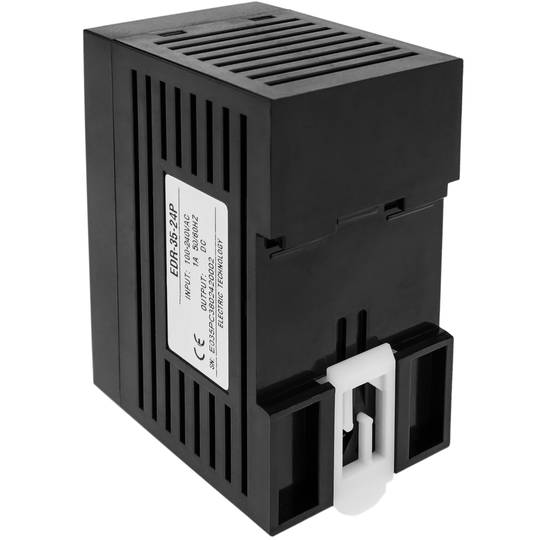
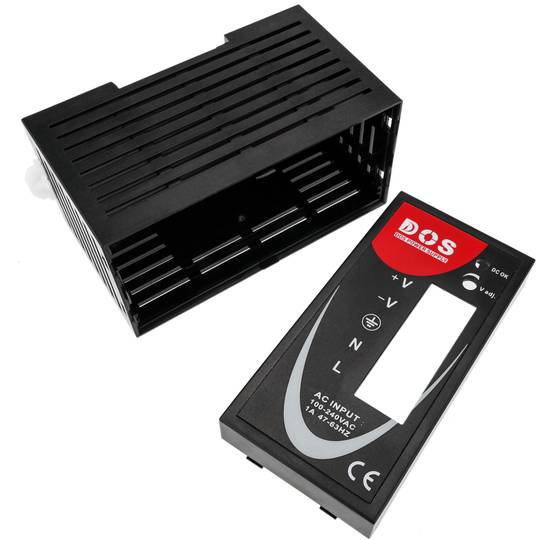
Power supply for Modbus module DIN rail 35 mm 12 VDC 3 A
REF: TJ091
Specifications
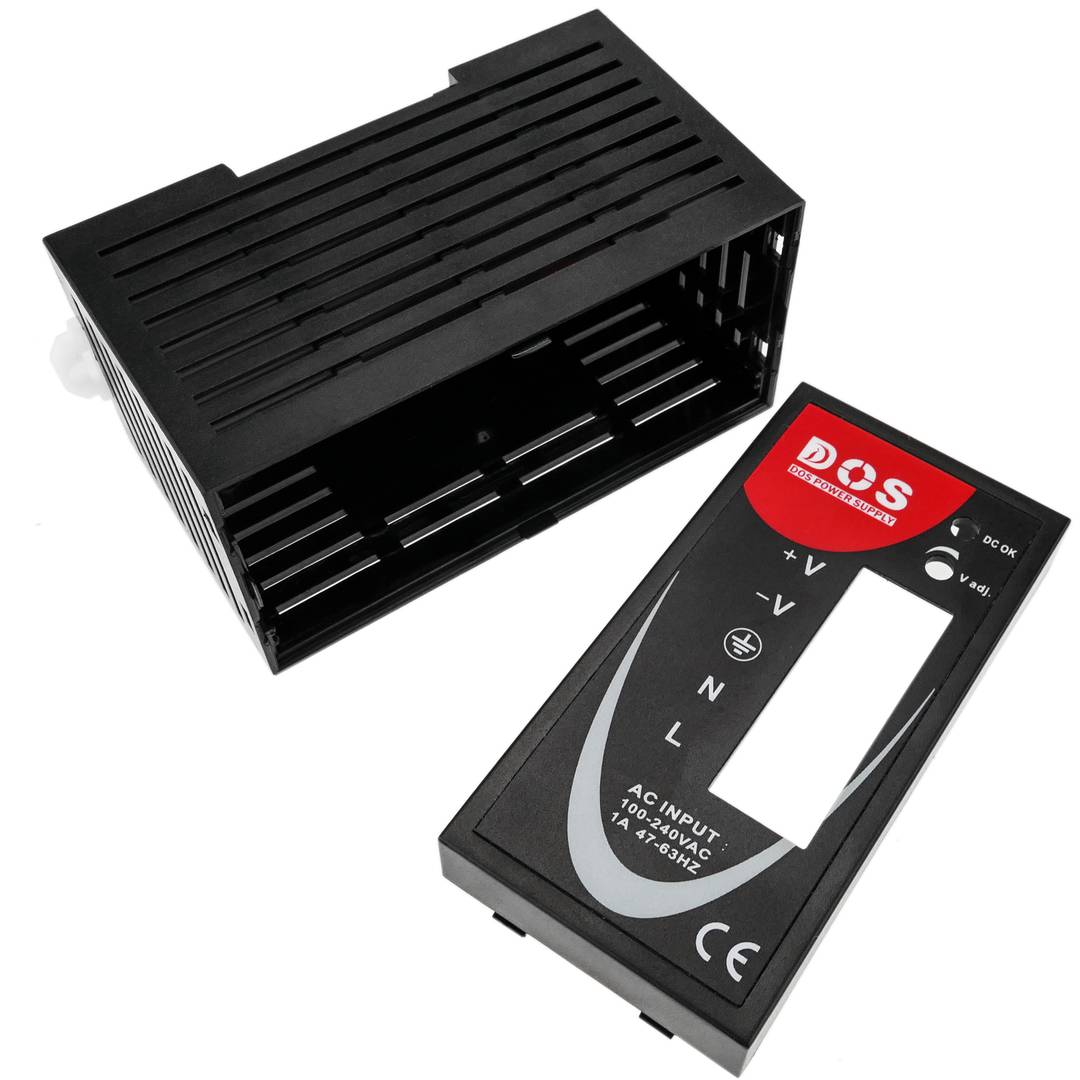
- Power supply for Modbus module and 35 mm DIN rail.
- Input voltage: 100-240 VAC.
- Output voltage: 12 VDC 4 A.
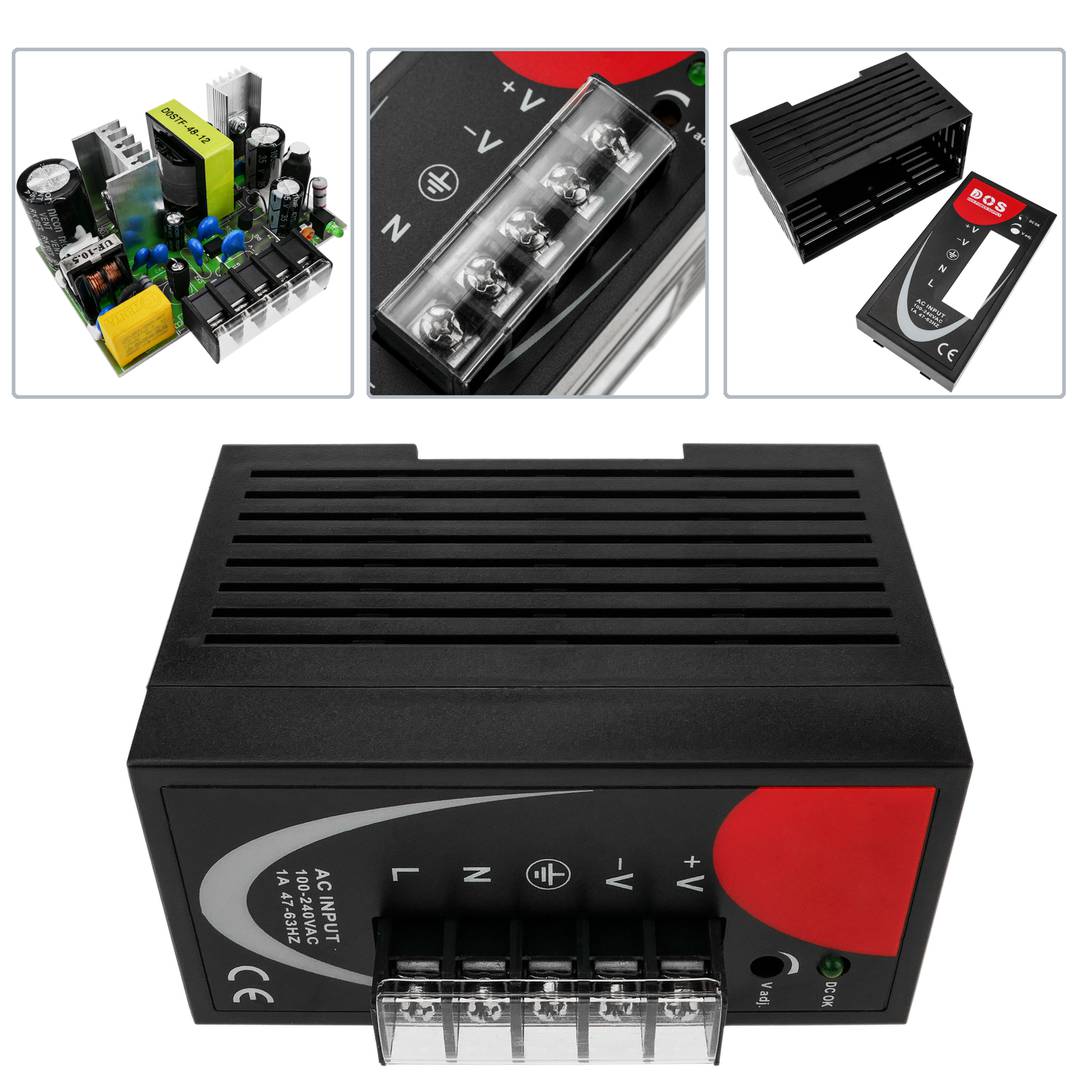
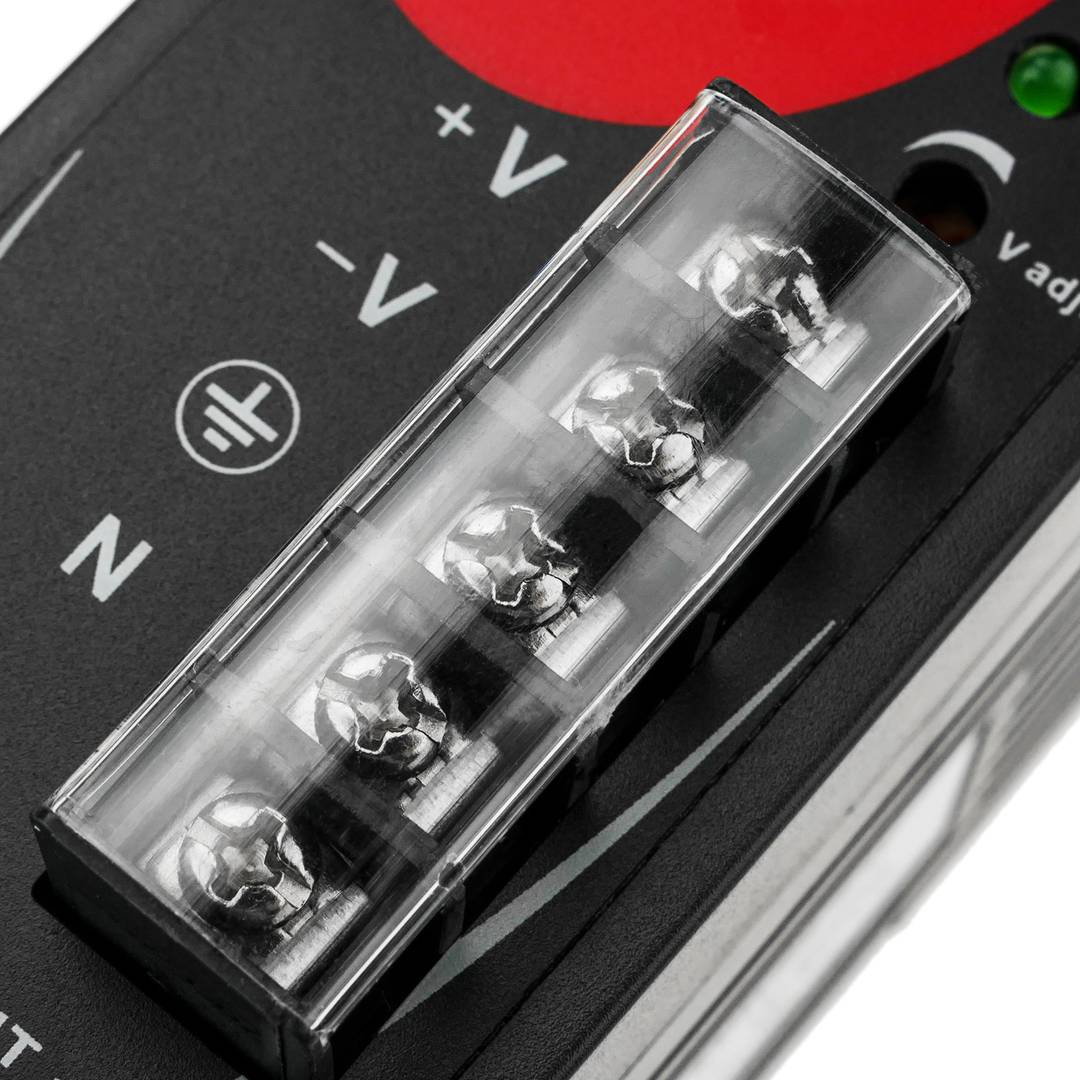
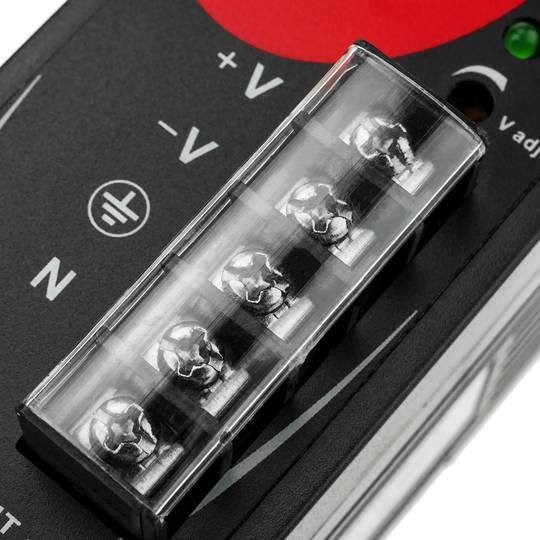
- Front connectors protected by transparent cover.
- Connectors prepared for 22 to 14 AWG wire.
PVP
€33.22
Price including VAT:
€33.22
PVD
€29.35
PVP: Retail price.
Check conditions.
PVP: Sale price to distributors.
Check conditions.
warranty
returns
safe
Specifications
- Power supply for Modbus module and 35 mm DIN rail.
- Input voltage: 100-240 VAC.
- Output voltage: 12 VDC 4 A.
- Front connectors protected by transparent cover.
- Connectors prepared for 22 to 14 AWG wire.
Keywords
Did not find what you were looking for? These topic could help you
More info
Power supply for Modbus module. Adaptable to 35mm DIN rail. Converts 100-240 VAC to DC. Front connectors, protected with transparent cover. AC sockets: line, neutral and ground and DC sockets: positive and negative.
Specifications
Specifications
- Power supply for Modbus module and 35 mm DIN rail.
- Input voltage: 100-240 VAC.
- Output voltage: 12 VDC 4 A.
- Front connectors protected by transparent cover.
- Connectors prepared for 22 to 14 AWG wire.
- Measurements (width x height x depth): 45 x 90 x 75 mm.
- Gross Weight: 265 g
- Product size (width x depth x height): 4.5 x 7.5 x 9.0 cm
- Number of packages: 1
- Packages size: 15.2 x 10.0 x 5.5 cm
Technical terms
- AWG
- DIN
- VDC
- DIN Rail
- VAC
AWG
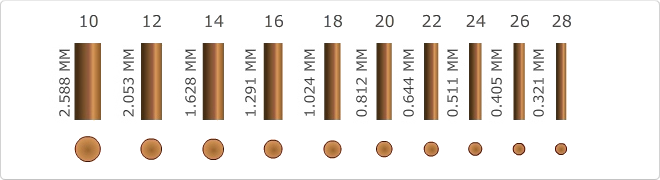
AWG stands for "American Wire Gauge". It's used to represent measures of cable length and section.
This is an AWG conversion table:
This is an AWG conversion table:
| AWG | Diam. mm | Area mm2 | AWG | Diam. mm | Area mm2 | |
| 1 | 7.35 | 42.40 | 16 | 1.29 | 1.31 | |
| 2 | 6.54 | 33.60 | 17 | 1.15 | 1.04 | |
| 3 | 5.86 | 27.00 | 18 | 1.024 | 0.823 | |
| 4 | 5.19 | 21.20 | 19 | 0.912 | 0.653 | |
| 5 | 4.62 | 16.80 | 20 | 0.812 | 0.519 | |
| 6 | 4.11 | 13.30 | 21 | 0.723 | 0.412 | |
| 7 | 3.67 | 10.60 | 22 | 0.644 | 0.325 | |
| 8 | 3.26 | 8.35 | 23 | 0.573 | 0.259 | |
| 9 | 2.91 | 6.62 | 24 | 0.511 | 0.205 | |
| 10 | 2.59 | 5.27 | 25 | 0.455 | 0.163 | |
| 11 | 2.30 | 4.15 | 26 | 0.405 | 0.128 | |
| 12 | 2.05 | 3.31 | 27 | 0.361 | 0.102 | |
| 13 | 1.83 | 2.63 | 28 | 0.321 | 0.0804 | |
| 14 | 1.63 | 2.08 | 29 | 0.286 | 0.0646 | |
| 15 | 1.45 | 1.65 | 30 | 0.255 | 0.0503 |