11/21/2025 9:22 p.m.
https://stage.cablematic.com/en/products/usb-to-rs232-db9-male-1-x-15-m-TS090/
https://stage.cablematic.com/en/products/usb-to-rs232-db9-male-1-x-15-m-TS090/
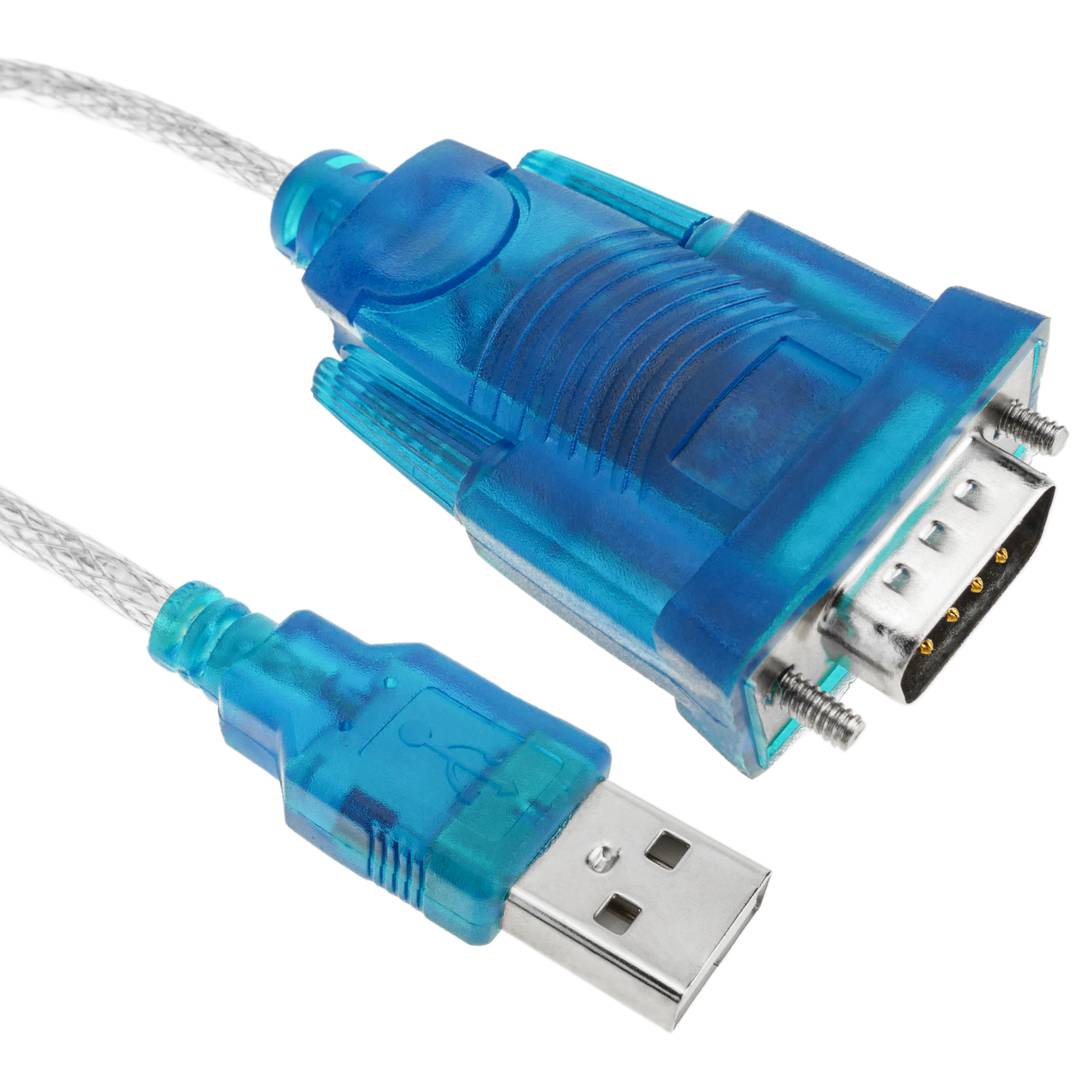
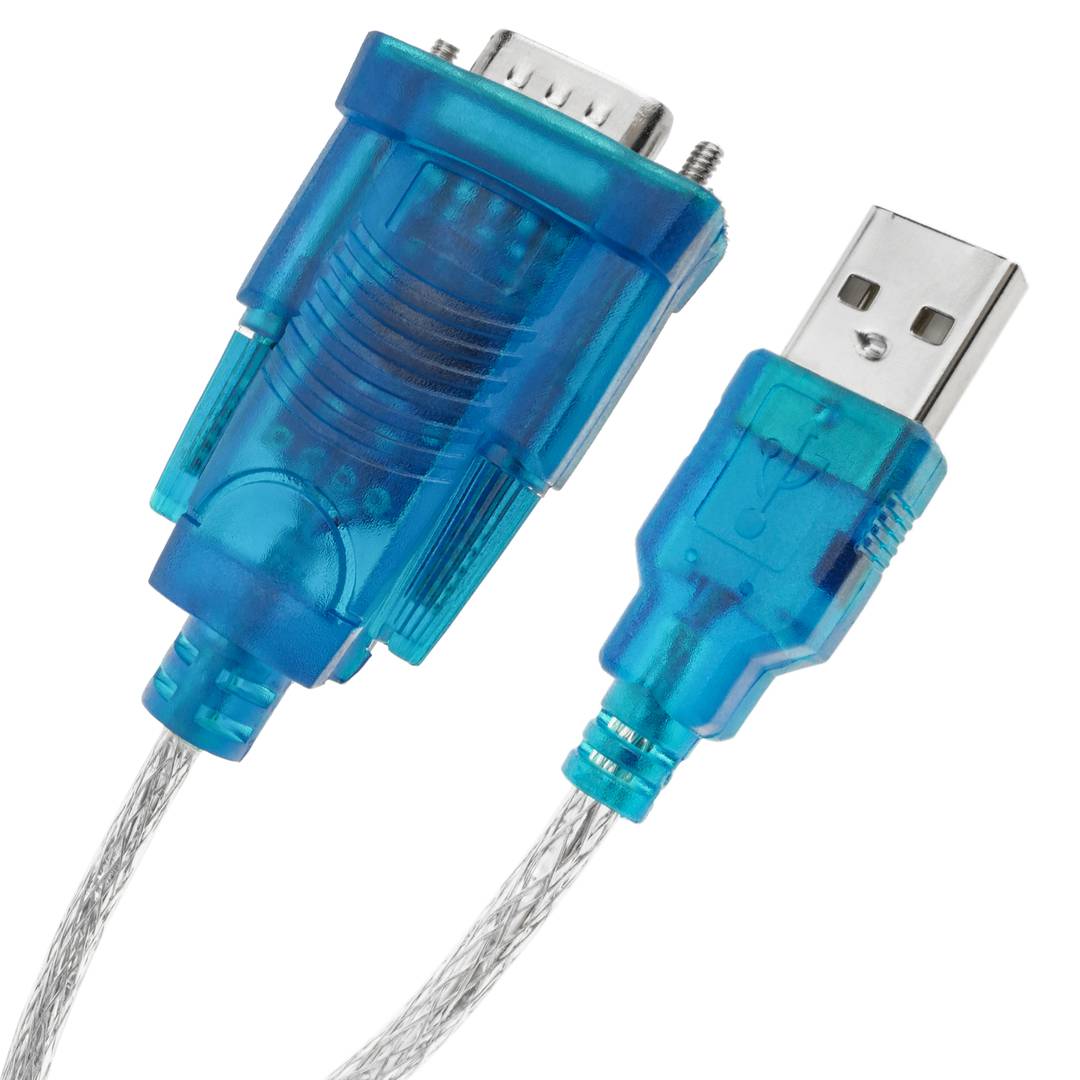
USB to RS232 DB9 male 1 x 1.5 m
REF: TS090
Specifications
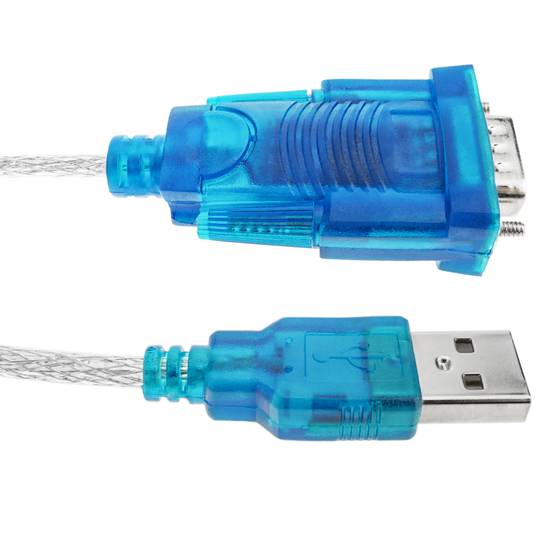
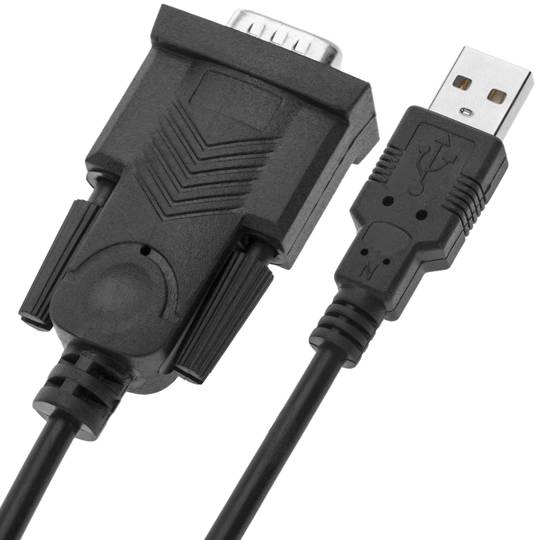
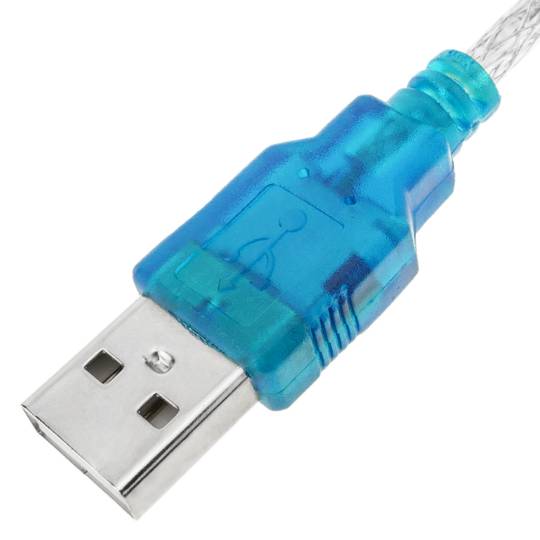
- USB to RS232 serial converter in 1.5 m long cable format.
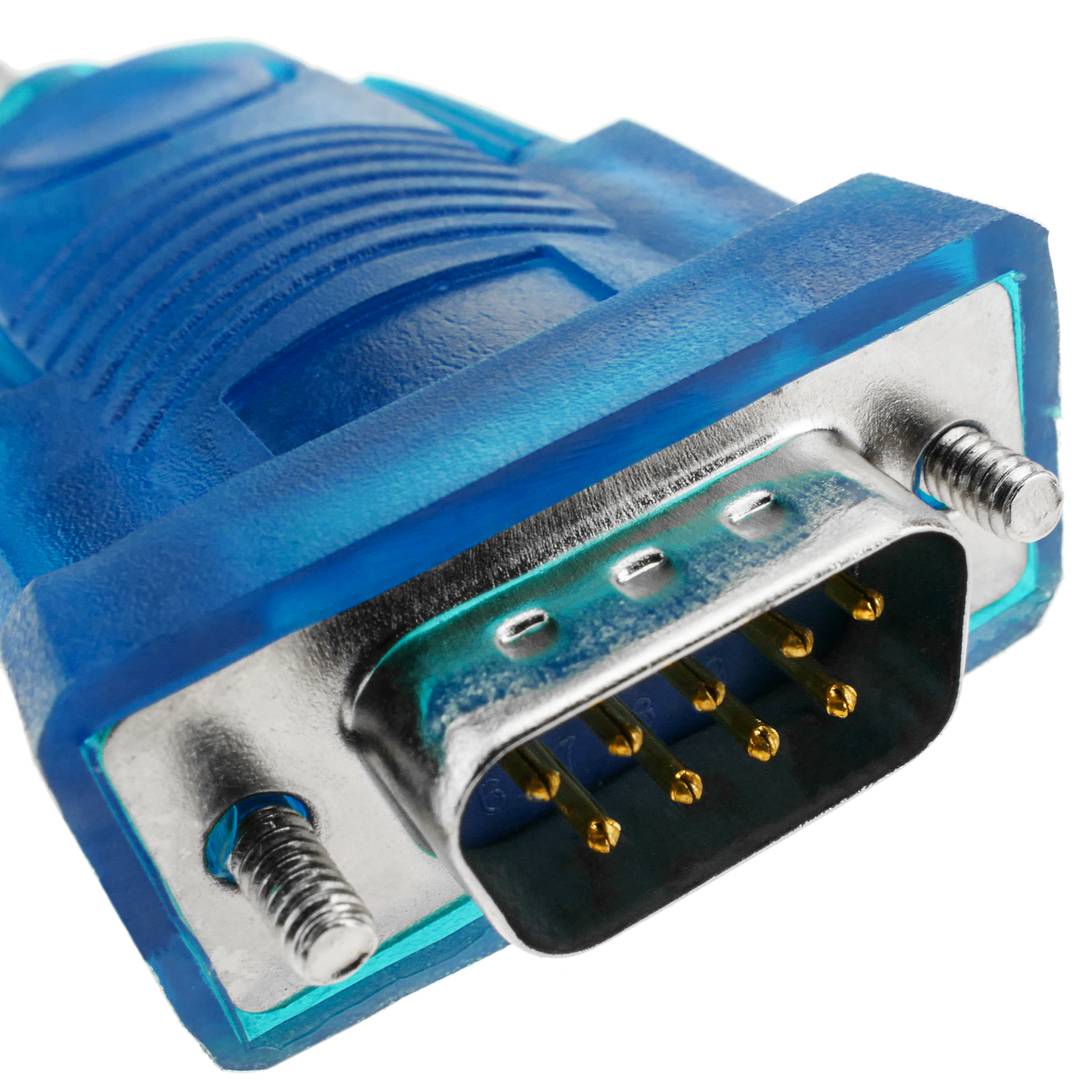
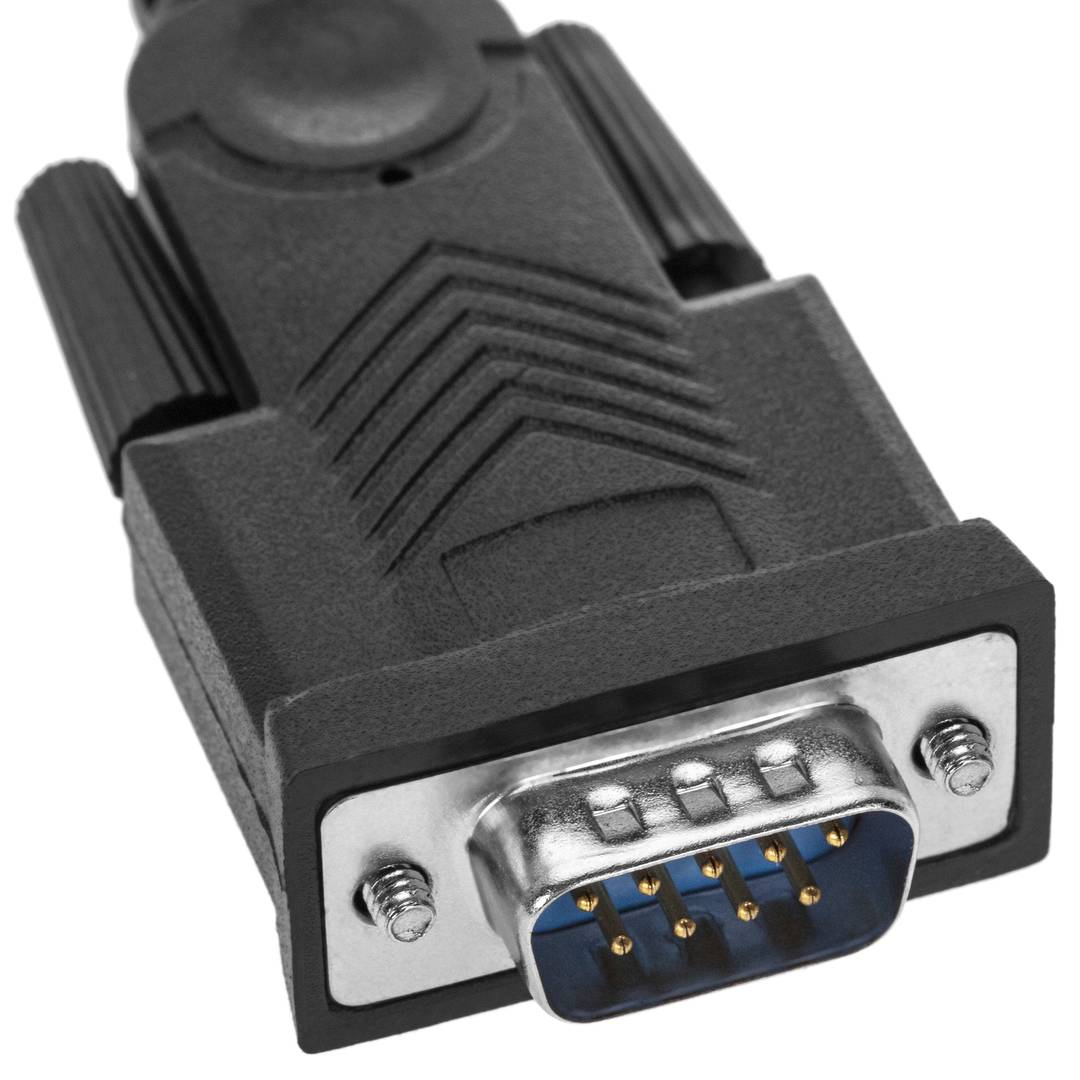
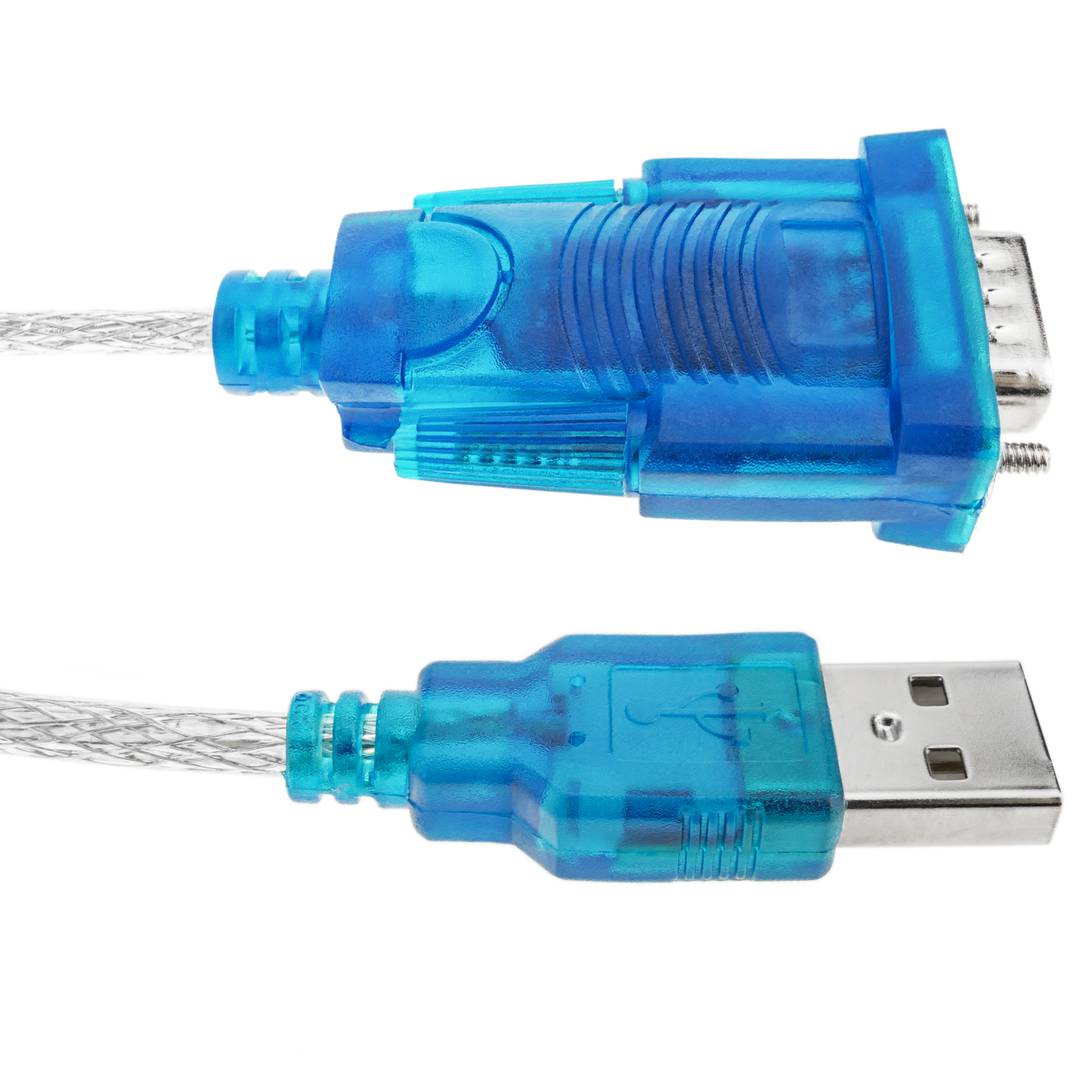
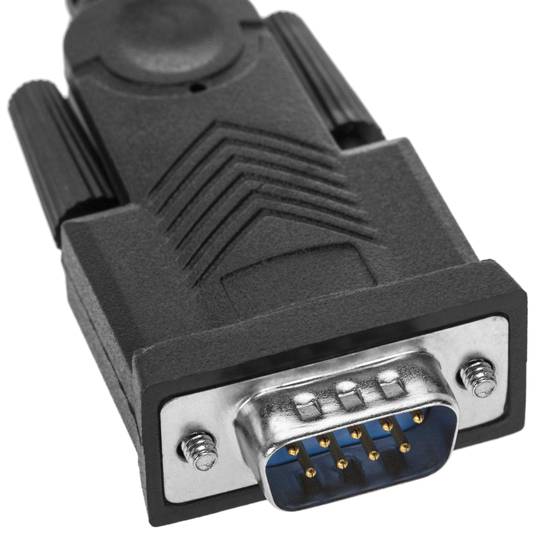
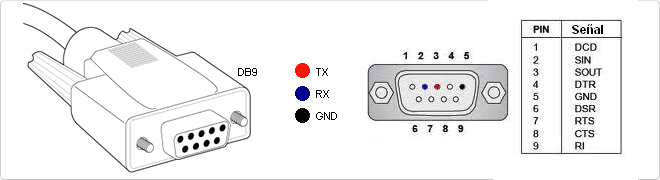
- At one end it has a USB type A male connector and at the other end of the conversion electronics and a male DB9 connector.
- PnP operation requiring no I/O port configuration or IRQ assignment.
- Maximum serial data transmission speed of 115.2 Kbps.
- Compatible with Windows, Mac OS and Linux environments.
![play_button]() Watch video
Watch video
More info
PVP
€5.30
Price including VAT:
€5.30
PVD
€4.26
PVP: Retail price.
Check conditions.
PVP: Sale price to distributors.
Check conditions.
warranty
returns
safe
Specifications
- USB to RS232 serial converter in 1.5 m long cable format.
- At one end it has a USB type A male connector and at the other end of the conversion electronics and a male DB9 connector.
- PnP operation requiring no I/O port configuration or IRQ assignment.
- Maximum serial data transmission speed of 115.2 Kbps.
- Compatible with Windows, Mac OS and Linux environments.
Keywords
Did not find what you were looking for? These topic could help you
More info
USB to RS232 serial converter in 1.5 m long cable format. At one end it has a USB type A male connector and at the other end of the conversion electronics and a male DB9 connector. PnP operation requiring no I/O port configuration or IRQ assignment. Maximum serial data transmission speed of 115.2 Kbps. Compatible with Windows, Mac OS and Linux environments.
Specifications
- USB to RS232 serial converter in 1.5 m long cable format.
- At one end it has a USB type A male connector and at the other end of the conversion electronics and a male DB9 connector.
- PnP operation requiring no I/O port configuration or IRQ assignment.
- Maximum serial data transmission speed of 115.2 Kbps.
- Compatible with Windows, Mac OS and Linux environments.
- Gross Weight: 51 g
- Product size (width x depth x height): 10.0 x 10.0 x 1.5 cm
- Number of packages: 1
- Packages size: 23.5 x 17.0 x 1.5 cm
Technical terms
- USB
- MicroUSB
- Mini USB
- Communication Series
- USB 3.0
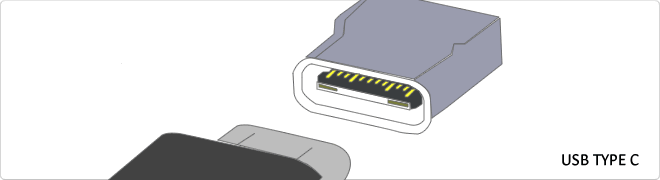
- Reversible USB Type-C
- RS232
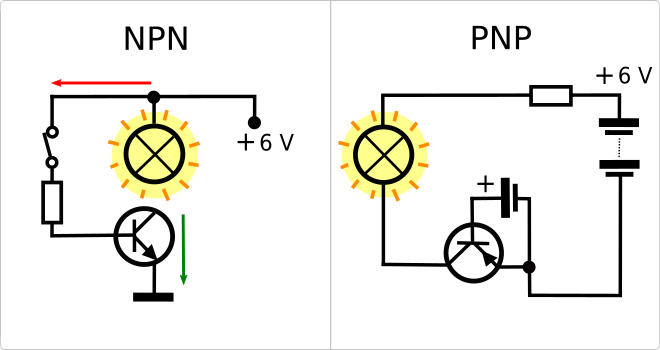
- Differences between PNP and NPN
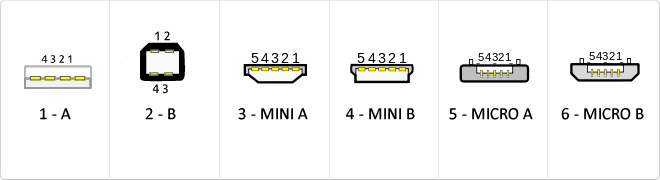
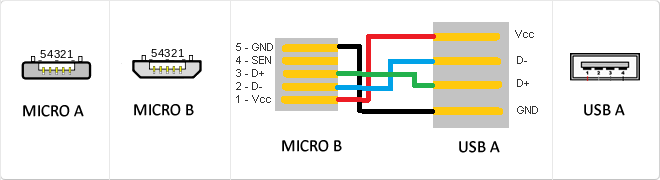
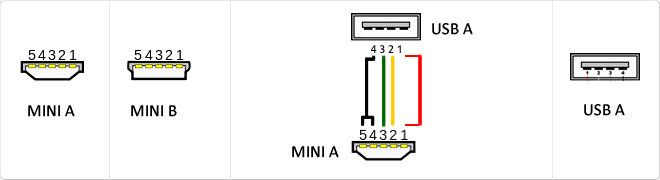
USB
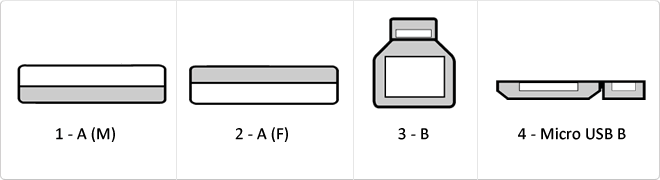
The USB (Universal Serial Bus) is a standard that defines the cables, connectors and used a bus to connect, communicate, computers, peripherals and electronic devices protocols Transmission Rates Low speed (USB 1.0). Transfer rate up to 1.5 Mbit/s (188 kB/s) used in keyboard, mouse ... transfer rate up to 12 Mbit/s (1.5 MB/s) High Speed ??(USB 2.0): Rate transferencia up to 480 Mbit/s (60 MB/s) SuperSpeed ??(USB 3.0) transfer rate up to 4.8 Gbit/s (600 MB/s) Connector Types 1 - USB type A (4 pin) 2. - USB type B (4 pin) 3 - Mini A (5-pin) 4 - Mini B (5-pin) 5 - Micro A (5-pin) 6 - Micro B (5-pin)